Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a revolution in the way technology interacts with companies, officials and individuals. From health diagnosis to personal marketing and automated financial services, AI affects all parts of our world. However, considerable responsibility comes with this incredible progress: to ensure that the AI system is designed, developed and distributed in ways that respect privacy and follow moral standards. This is the place where AI privacy ethics plays an important role.
When AI affects all aspects of life, questions of privacy and artificial intelligence are no longer abstracted; instead, they suppress the concerns. Organizations should balance innovation with responsibilities and ensure that they use AI Ethics to use AI while protecting user data. Failure to do so not only puts risks at risk but also invites legal consequences and known harm.
In this blog, we will learn about the challenges of best practices for organizations to enforce AI person-protection morale, AI Ethics principles and responsible AI strategies.
According to the World Economic Forum, over 78% of companies are now exploring or implementing AI technologies in their operations, up from 55% just a year earlier.
Understanding AI Privacy & Ethics
AI ethics refers to the ethical principles and guidelines that control how artificial intelligence systems should be developed and used. Originally, AI ethical questions are such as, “How should AI make decisions?” How do we ensure justice and openness? How can we protect individuals from damage due to AI?
On the other hand, privacy and artificial intelligence focus especially on how AI systems handle individual data. The AI system depends on large amounts of information to function effectively. This data often includes sensitive personal details such as financial records, health information, and browsing and site data. This misuse or abuse of information can lead to serious privacy violations.
AI ethics and privacy principles work together to inform the manager of AI development. AI ethics gives a moral direction to AI developers, while a privacy-first approach to personal data tells us that technology should function in a way that respects human rights and dignity. Organizations that sequentially incorporate these two components of their AI product development method will build trust and promote a sustainable growth path.
Why AI Privacy Ethics Matters
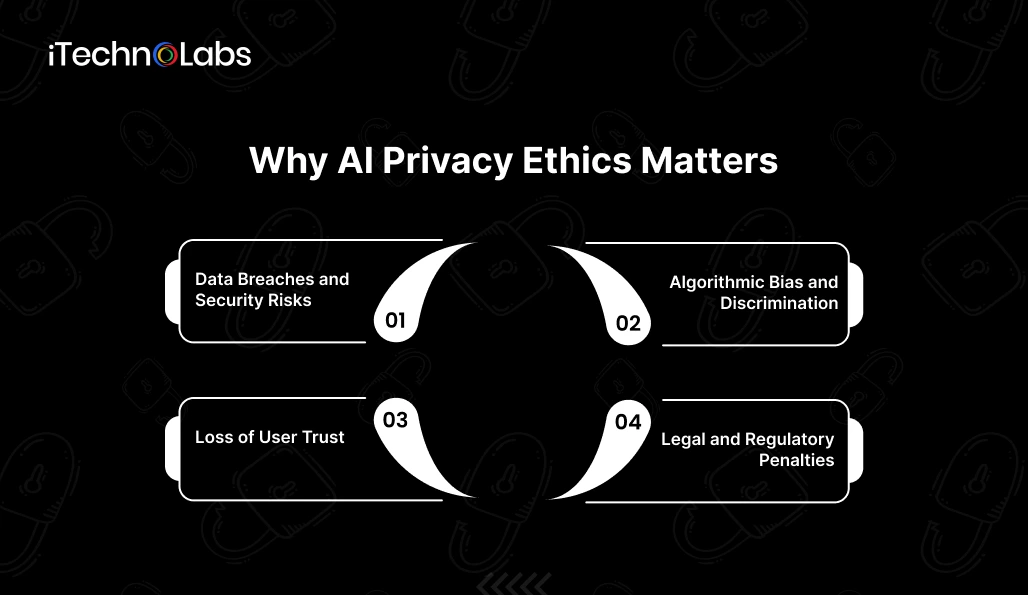
The effectiveness of AI systems depends largely on how they are applied. While data are the foundation for new ideas and better processes, they come with a downside that is risk and loss. AI can win over the aforementioned security, fairness, trust in users and regulation even if the privacy ethics are against them.
1. Data Breaches and Security Risks
The AI initiative involves using large amounts of sensitive personal information, making them attractive goals for cyber criminals. Without sufficient security measures, to include encryption, access control and continuous monitoring, data violations may be compromised by personal information. Focusing on AI ethics around privacy will help protect the data from protection and unauthorized access. In addition, it will increase confidence in increasing the relationship with each organization with users and stakeholders.
2. Algorithmic Bias and Discrimination
AI models use historical data sets to identify patterns. If these data sets have prejudice, AI may unconsciously eliminate or increase discrimination, which can affect areas such as work, borrowing and health care. Applying AI morality and justice measures reduces prejudice, promotes equity and ensures that the AI system is responsible and only determines.
3. Loss of User Trust
Consumers quickly know how organizations use personal information. Abuse, lack of openness or immoral AI decisions can destroy self-confidence, damage reputation and reduce user loyalty. Including privacy and artificial intelligence principles helps organizations maintain reliability, strengthen conditions and promote long-term commitment with users.
4. Legal and Regulatory Penalties
New regulations like GDPR and CCPA have set very high, even impossible, standards for collecting and processing data and obtaining consent. Errors and negligence in this regard can lead to costly penalties, legal actions and losses of goodwill for the companies involved. AI Personal Security comes to the rescue of organizations in the maze of legal compliance and at the same time keeps the morals of sensitive data. Subsequently, it lessens the risk and promotes ethical AI use.
By incorporating AI personal security ethics, organizations can reduce the risk, increase justice, promote openness and build responsible and reliable AI systems.
Key Principles of AI Privacy Ethics
Organizations implementing responsible AI development should stick to the basic guidelines that protect privacy and encourage ethically sound practices. The next table presents the overall principles, their meanings, and the ways they can be put into practice.
| Principle | Definition | Practical Implementation |
| Transparency | Clear communication about how AI systems collect, process, and use data | Publish privacy policies, provide explanations of AI decisions, and maintain audit trails |
| Fairness | Ensuring AI decisions are unbiased and equitable | Monitor datasets for bias, test models on diverse populations, implement corrective measures |
| Data Minimization | Collect only the data necessary for a task | Limit data collection to required fields, anonymize unnecessary details |
| Security by Design | Integrate strong security measures from the outset | Encrypt data, anonymize sensitive info, implement access controls |
| Accountability | Developers and organizations are responsible for AI outcomes | Document processes, conduct regular audits, establish reporting channels |
| Respect for Human Rights | Ensure AI systems do not harm individual rights or dignity | Avoid discriminatory practices, prioritize user consent, and assess social impact. |
This table helps readers quickly understand the essential pillars of AI privacy ethics and see how they can be applied in real-world scenarios.
Challenges at the Intersection of Privacy and Artificial Intelligence
While the AI person protection nets provide a framework, these principles are difficult to perform. The following table provides a summary of some common challenges as well as potential (and promising) approaches to mitigation:
| Challenge | Impact | Mitigation Strategy |
| Bias in Training Data | Discrimination in AI decision-making | Use diverse datasets, audit models for bias, implement corrective measures |
| Explainability Issues | Difficulty understanding AI decisions | Implement explainable AI techniques, provide clear decision rationales |
| Cross-Border Data Regulations | Legal risks when operating globally | Ensure compliance with local and international privacy laws |
| Data Ownership and Consent | Unclear rights over personal information | Obtain informed consent, define clear ownership policies |
| Emerging Technological Threats | Risk from AI-Fremskits such as Deepfakes and Predictive Surveillance | Regular risk assessments, adopt privacy-preserving technologies |
This table allows readers to grasp at a glance the key risks in AI development and how they can be addressed.
Also, read: AI Voice Agents: Create Smart Assistants with AI Voice Generators
Implementing Ethical AI Practices in Organizations

Organizations that have AI privacy ethics as their focus have a competitive advantage as they build trust and credibility. They can implement responsible AI practices across the entire development lifecycle by embedding ethical strategies into actionable practices. Organizations can take several key actions, which are
1. Adopt Ethical AI Frameworks
Creating an internal ethical AI structure adjusts each stage of AI development with moral and legal principles. This includes data collection, model training, distribution and monitoring. Framework defines organizational standards for justice, openness, and responsibility and helps the teams make responsible decisions while protecting sensitive information and maintaining public trust.
2. Use Privacy-Preserving Techniques
Privacy preservation technique lets the AI system learn from data without highlighting personal information. While maintaining AI performance, methods such as Federated Learning, Differential Privacy and Safe Calculation of Several parties reduce the risk. By integrating this practice, organizations show an obligation to privacy and artificial intelligence and reduce potential abuse of personal data.
3. Conduct Regular Audits
Regular audits are necessary to ensure that AI systems remain ethical, fair and secure. An audit model can detect bias, uncover privacy absorption and verify compliance with current laws and standards. Independent evaluation, influence assessments and responsibility audits can keep organizations obliged to AI ethics when establishing reliable relationships with affected stakeholders and consumers.
4. Empower Users with Data Control
Checking users on their data improves openness and trust. The functionality that allows users to see, change, or remove strengthens individuals and shows a commitment to the moral use of AI. Easily accessible and transparent privacy rules, with user-friendly control, are important components of responsible privacy and AI initiatives.
5. Provide Training and Awareness
Training of employees regarding AI ethics and best practices for privacy creates a culture of responsibility. It is important for team awareness to understand their role in building ethical AI systems, which can come from consciousness campaigns, workshops and training programs. By putting money into education and awareness of ethical behavior, organizations build responsibility and employee awareness of their responsibility and organization alignment of AI initiatives with legal and social expectations.
For example, a healthcare AI company incorporated differential privacy into its patient data analytics models to ensure that no patient can be identified from their records. This approach allowed the company to create accurate predictive models while completely respecting the patient’s privacy.
Global Regulations and AI Ethics Compliance
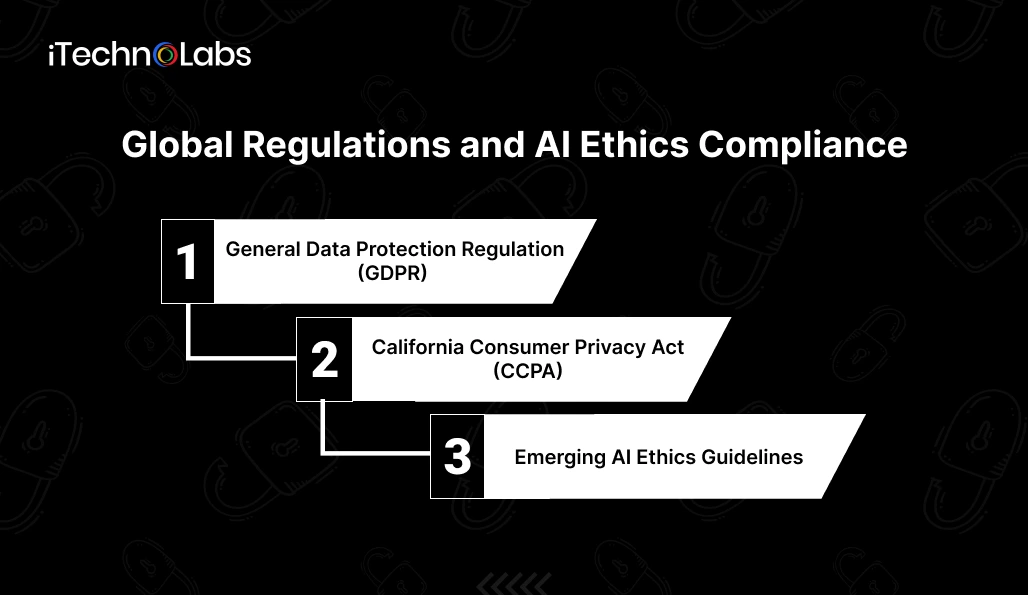
Legal frameworks are essential for maintaining the ethical norms put in place to assure AI’s ability to respect privacy. The way organizations use user data must conform to local and global laws. Compliance allows organizations to establish user trust while minimizing legal liability. The following represents just a handful of the existing regulations and policies affecting an ethical AI.
1. General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) establishes exact rules for the collection, processing and storing of individual information in the EU. This is focused on transparency, consent and individual rights and means it captures a sense of an individual’s knowledge being checked. The AI system needs to reflect GDPR compliance to avoid severe penalties and to demonstrate a commitment to ethical data practices.
2. California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
The CCPA broadened the rights of California residents with respect to their personal information, including the option to opt out of selling data and to request deletion. AI companies operating in the US need to secure systems so they are respectful of privacy and artificial intelligence principles to provide transparency and user control and to respect these rights.
3. Emerging AI Ethics Guidelines
Governments and organizations across the globe are setting up ethical guidelines for AI as a measure to back ethical AI development. The OECD principles on AI and the EU AI Act are the main frameworks for AI ethical standards that are centered on transparency, accountability, fairness, and privacy. Integrating AI activities with these frameworks is very important not just for presenting an ethical AI but also for creating trust among the stakeholders in the tech.
On the other hand, observance of these rules and ethical norms by companies will not only help them to cut down legal risks but also promote fairness and public confidence in AI tech, besides showing a proactive stance on AI ethics.
The Future of AI Privacy Ethics

The future of AI gives a huge promise but should be directed by strong moral principles. Organizations and decision-makers believe that responsible AI is important for long-term innovation, trust and social gains. Large trends in the development of privacy and artificial intelligence:
1. Integration of Ethics into AI Design
Ethical ideas are quickly built into the AI design instead of being treated later. Developers now prioritize justice, openness and responsibility in the AI life cycle and ensure that the AI systems work responsibly and respect privacy and social norms.
2. AI as a Trust Enabler
Companies that use AI practices can vary in competitive markets. By demonstrating openness, justice and commitment to privacy and artificial intelligence, organizations create strong faith with users, stakeholders and regulators, creating long-term and commercial benefits.
3. Global Collaboration
Policymakers, mentors, and stakeholders from the private sector are joining forces to come up with ethical frameworks and standards for AI. Global collaboration can facilitate regulation by creating a route to aligned regulations, lowering the likelihood of privacy concerns arising from cross-border operations, and guaranteeing that AI systems are governed by the same values of justice, responsibility, and openness.
4. Technological Advancements
Emerging AI technology, such as explainable AI, secrecy protection machine learning, and automatic bias, improves the moral distribution of the AI system. These technologies help organizations to maintain compliance with AI person protection morality, protect sensitive data and improve model transparency for users.
5. Sustainable Innovation Through Ethics
As artificial intelligence (AI) becomes ubiquitous in our everyday lives, it is essential that we maintain a focus on ethical principles and protections of privacy. Responsible AI can be understood as ensuring that the innovations we pursue are sustainable, processed reliably and effectively aligned to our social values so that we may rightfully improve our organizations’ approaches to utilizing AI while simultaneously minimizing societal risk for individuals and communities overall.
Also, read: How AI-powered digital transformation is Revolutionizing Businesses
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence technology provides unique opportunities to replace technology industries, improve the decision and increase daily life. However, it comes with a moral responsibility that these techniques are responsible for handling and protecting user data. Preference to AI-person protection morale ensures that the systems are not only effective and advanced but also fair, transparent and respectable for personal rights. By applying privacy and artificial intelligence principles throughout the life cycle of perfection and monitoring from data collection and AI model training, the organization can reduce the risk, prevent prejudice and maintain regulatory compliance.
Using AI ethics is outside of meeting legal requirements; It provides a competitive advantage. Companies engaged in moral practice create user confidence, strengthen their reputation and stand out in competing markets. In the development of the system, AI privacy morality and privacy and artificial intelligence integrate, organizations promote permanent innovation, protect human dignity and ensure that technology develops responsibly and the same for everyone.
FAQ
1. What are AI privacy ethics, and why are they important?
AI privacy ethics refers to the principles and practices that ensure artificial intelligence systems handle data responsibly, fairly, and transparently. It is important because it protects user privacy, prevents bias, and builds trust in AI technologies.
2. How can organizations ensure AI respects privacy?
Organizations can ensure privacy by collecting only necessary data, using anonymization and encryption, implementing privacy-preserving AI techniques, and giving users control over their data.
3. What are the key principles of AI ethics?
Key principles include transparency, fairness, data minimization, security by design, accountability, and respect for human rights. Following these principles ensures ethical AI development.
4. What are common challenges in implementing AI privacy ethics?
Challenges include biased training data, lack of explainability, cross-border data regulations, unclear data ownership, and emerging threats like deepfakes or predictive surveillance.
5. How do privacy and artificial intelligence impact users?
Privacy-focused AI ensures users’ personal data is protected, decisions are fair and transparent, and individuals have control over how their information is used, enhancing trust and confidence in AI systems.